Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
페이지 정보
작성자 Alvin 작성일25-04-23 03:18 조회13회 댓글0건관련링크
본문
A cardiac stress test, also known as a myocardial perfusion scan, is a heart assessment that uses small amounts of radioactive material to assess blood flow to the heart muscle. This test is commonly used to diagnose heart attack, a condition also known as a heart attack, where the blood flow to the heart muscle is severely reduced or blocked.
During a cardiac stress test, a radioactive dye is injected into the bloodstream through an catheter. The dye accumulates in the cardiac tissue, making it visible on the image. The patient is then asked to walk on a stationary bike while their blood pressure and blood pressure are monitored. This physical assessment is designed to mimic the physical demands of daily life, allowing the doctor to see how the heart muscle responds to increased activity.
The image is then performed using a special camera, which takes images of the cardiac tissue as it accumulates the radioactive dye. The results are analyzed to show tissue damage that are receiving adequate blood flow and those that are not. heart attack is diagnosed when tissue do not receive enough blood flow, leading to the death of cardiac muscle.
A nuclear heart scan is typically performed in two stages: rest and اسکن هسته ای قلب stress. During the rest stage, the patient's blood pressure and blood flow are monitored while they are at rest. The radioactive dye is then injected, and pictures of the heart muscle are taken. During the stress stage, the patient exercises while their heart rate and blood flow are monitored, and additional pictures are taken.
The advantages of a nuclear heart scan include its ability to diagnose myocardial infarction at an early point, before conditions become severe. This allows for timely care to prevent long-term damage to the heart. The test is also non-invasive and relatively quick, taking about 1 hour to complete.
However, as with any medical test, a cardiac stress test has its limitations and risks. Some patients may experience side effects from the radiation marker, such as mild discomfort or discomfort. Additionally, the test may not be suitable for certain patients, such as those with kidney disease or pacemakers.
Overall, a nuclear heart scan is a valuable medical assessment for diagnosing cardiac myocardial infarction. It allows doctors to assess the blood flow to the cardiac tissue and identify tissue damage or disease. By diagnosing heart attack at an early stage, patients can receive timely care and prevent long-term damage to their heart.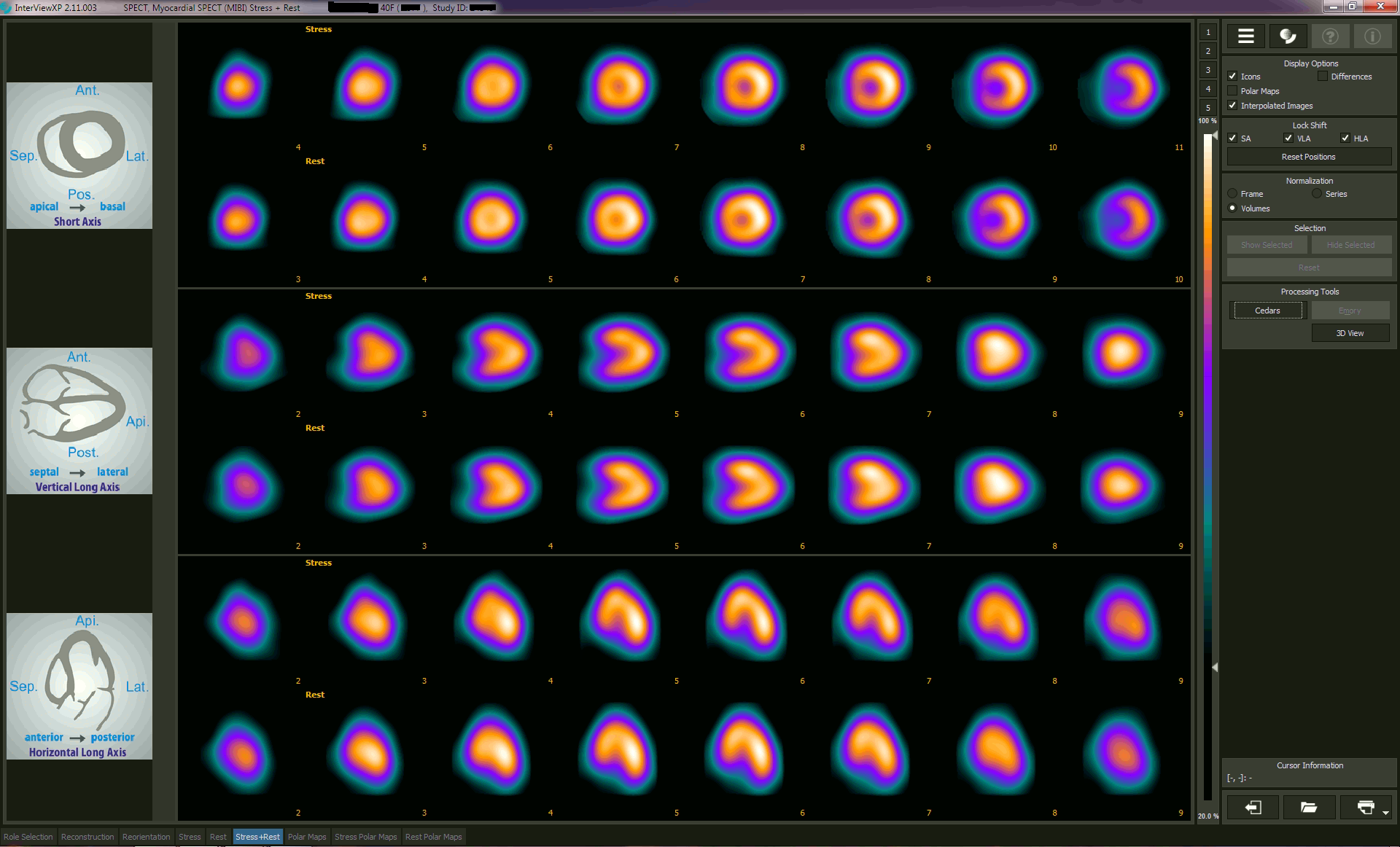
During a cardiac stress test, a radioactive dye is injected into the bloodstream through an catheter. The dye accumulates in the cardiac tissue, making it visible on the image. The patient is then asked to walk on a stationary bike while their blood pressure and blood pressure are monitored. This physical assessment is designed to mimic the physical demands of daily life, allowing the doctor to see how the heart muscle responds to increased activity.
The image is then performed using a special camera, which takes images of the cardiac tissue as it accumulates the radioactive dye. The results are analyzed to show tissue damage that are receiving adequate blood flow and those that are not. heart attack is diagnosed when tissue do not receive enough blood flow, leading to the death of cardiac muscle.
A nuclear heart scan is typically performed in two stages: rest and اسکن هسته ای قلب stress. During the rest stage, the patient's blood pressure and blood flow are monitored while they are at rest. The radioactive dye is then injected, and pictures of the heart muscle are taken. During the stress stage, the patient exercises while their heart rate and blood flow are monitored, and additional pictures are taken.
The advantages of a nuclear heart scan include its ability to diagnose myocardial infarction at an early point, before conditions become severe. This allows for timely care to prevent long-term damage to the heart. The test is also non-invasive and relatively quick, taking about 1 hour to complete.
However, as with any medical test, a cardiac stress test has its limitations and risks. Some patients may experience side effects from the radiation marker, such as mild discomfort or discomfort. Additionally, the test may not be suitable for certain patients, such as those with kidney disease or pacemakers.
Overall, a nuclear heart scan is a valuable medical assessment for diagnosing cardiac myocardial infarction. It allows doctors to assess the blood flow to the cardiac tissue and identify tissue damage or disease. By diagnosing heart attack at an early stage, patients can receive timely care and prevent long-term damage to their heart.

댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.